Overview:
The Cisco TelePresence Exchange System is an integrated telepresence and video service-creation platform that can help service providers and strategic partners create and manage secure, cloud-based, multitenant video collaboration services.
Software-based, the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System is powered by a fully redundant architecture that can dramatically reduce time to market and improve operating margins for business video and telepresence services such as secure business-to-business calling, hosting services, and scheduled and rendezvous (reservation-less or virtual meeting room) multimedia conferencing targeted at a broad universe of video endpoints, from immersive rooms to soft-client endpoints for mobile devices. It does so through a set of modular features that simplify the tailoring of video services to the service provider market and streamline operations with a solution-focused management interface and open application programming interfaces (APIs) that ease the solution integration with service providers' business and operational support systems.
The Cisco TelePresence Exchange System intelligently optimizes call routing and conference resource selection for globally distributed customers using distributed and strategically placed media switching and transcoding resources. It optimizes the resource selection based on the types of endpoints joining a meeting in order to yield the lowest network transport and per-port cost with the best possible user experience. The conferencing application aggregates conference resources based on pools of available ports to create a highly available conferencing solution that allows you to add or remove resources without affecting service. A centralized administration interface provides a single point of access for solution management, billing, conference resource capacity planning, and system administration.
Based on proven multitenant technology, powered by a fully redundant and scalable architecture, and controlled by a modular licensing model, the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System allows service providers to view telepresence services as building blocks that they can use to expand their business based on market demand. In addition, the system is an open platform with APIs that allow service providers and partners to build new applications to customize and complement the overall solution. Readily available through the Cisco Developer Network, these APIs are currently available to all customers.
In the fast-paced video market, the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System dramatically reduces technology risk through a validated architectural approach and allows service provider partners to focus on their business and differentiation strategy rather than on the underlying technology challenges.
- Helps increase revenue opportunities
- Accelerates growth of telepresence and video communities on the network
- Improves efficiency of service delivery and resource management for multitenant video services
- Delivers value-added conferencing and business-to-business services for video and telepresence
- Supports selling new, cloud-based solutions to deploy pervasive video, and expand into bring-your-own-device (BYOD)
Business Benefits
The Cisco TelePresence Exchange System and Cloud Solution architecture helps reduce deployment costs and operational risk through a modular approach that integrates:
- Media
- Service control
- Hosted applications and exchange management
Partners can also introduce a range of basic and advanced media services for telepresence, including highly secure intercompany calls, as well as:
- Multimedia conferencing, including rendezvous and scheduled calls
- Interoperability subscriber services and standards-based video (H.323 and SIP endpoints)
- Line side service registration and feature delivery for hosted endpoint services
- Wholesale services, including service provider interconnect
- Additional value-added, shared media services, and customized service options are also available
New Solution Options
Pervasive Conferencing from the Cloud
Expanded options help partners deliver video-as-a-service conferencing, with on-demand virtual meeting rooms. This creates simple-to-use consumption models, and accelerates the adoption of pervasive conferencing.
These new virtual meeting rooms let enterprises have video meetings any time, from anywhere, with simple set-up and management control.
Virtual Meeting Rooms deliver additional benefits, as they:
- Complement on-premise customer deployments
- Integrate with Cisco Hosted Collaboration Solutions
- Offer affordable, predictable service models
- Support pay-per-month and pay-as-you-grow commercial offers
Service Enablement
A flexible service-creation platform for multitenant cloud-based business video-as-a-service solutions, the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System supports the development of a broad portfolio of video call and conferencing subscription services. Providers can introduce a range of basic and advanced services to deliver secure intercompany calls, multimedia conferencing and virtual meeting room services, interoperability services, high-touch services such as personalized concierge, and active or dynamic meeting management services.
Designed to complement existing network and conferencing solutions, the system is intended to aid in the accelerated growth of telepresence and video communities on provider networks and in the expansion of the global network for video from high-end immersive rooms to mobile clients and desktop video stations.
Features and Benefits:
The Cisco TelePresence Exchange System is a feature-rich platform that offers the following features and benefits:
System Management and Scalability
- Multitenancy: Service providers can support multiple business customer organizations from a single Cisco TelePresence Exchange System deployment. The system segments organization information and policy control for business-to-business communication and conferencing services.
- Optimized call routing: The system optimizes call routing for endpoints and network bandwidth to improve network economics and user experience across geographies and across service provider networks. The meeting-scheduling APIs also allow third-party applications to intelligently instruct the system to host meetings using the resources closest to the majority of the session participants.
- Resource management and pooling: The Cisco TelePresence Exchange System manages the allocation of media resources for scheduled and rendezvous (reservationless) conferencing services. By clearly separating the service-control components from the media-processing components, the system can consistently implement a pooling resource-management strategy for all media resources, including Cisco TelePresence Server, multipoint control units (MCUs), and interactive-voice-response (IVR) systems. The net result is a fully redundant solution where the system always selects the most available resource to handle a session in real time, so that even when a media resource failure affects existing sessions and meetings, as long as additional media resources are available the affected parties will be able to redial and continue from where their conversation was terminated.
- Conference resource optimization: In addition to the resource management and pooling function, the system offers the ability to create Differentiated Services (DiffServ) based on configurable resource subscriptions. The system offers the ability to slice the resources into guaranteed and best-effort pools with granular meeting-level or organization-wide service options. Guaranteed pools offer customers guaranteed availability of resources for their meetings when they need it, while Best-effort pools can be oversubscribed at many different levels based on customer needs. Meeting capacity can also be calculated on a meeting-level or organization-wide for further service flexilibility to enable pervasive video. Meeting size can be enforced at attend time on a per meeting basis by calculating maximum number of screens allowed based on scheduled parameters in order to manage capacity and optimize ROI by allocating resources as needed. Organization wide services can also be supported through the allocation of a fixed number of virtual ports which can be assigned and utilized for as many rendezvous or scheduled meet-me meetings as necessary at specified service levels. This option allows users to maximize shared port utilization and optionally pay premium rates for usage overages. Flexible and configurable attend-time and organization wide port-allocation algorithms allow providers to optimize service levels and reserve ports dynamically, providing oversubscription options and increased ROI.
- Multiregion support: Service providers can distribute media resources into different geographical regions to segregate customers and endpoints based on the region they are in. In addition, they can schedule meetings based on the region where most customers reside to optimize resource usage.
- Exchange management: The Cisco TelePresence Exchange System offers service providers a comprehensive management solution. Solution-management interfaces include Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), a web-based management and provisioning administrator portal, and flow-through provisioning options for some media elements such as the Cisco TelePresence MSE 8710 and Cisco TelePresence Server MCUs. Over time the flow-through provisioning capabilities of the product will expand to other network and media elements in order to support the service scale. In addition, the health of every resource is continuously monitored. The Cisco TelePresence Exchange System proactively takes a faulty resource out of service to avoid possible effects on service availability. The system exposes these fault conditions through its administration and SNMP interfaces so that service providers can capture these events and produce appropriate alarms.
- Policy management: The Cisco TelePresence Exchange System allows for flexible policy configurations for call routing and call treatment. The administration system allows the capability to add direct-dial white-list policy groups as well as the ability to configure inter-service provider call-policy decisions.
- Call detail records (CDRs): The Cisco TelePresence Exchange System is a centralized control point for management, billing, and administration. The system provides real-time CDRs for all calls traversing the exchange solution. With a single point of collection for call information, service providers can easily aggregate and correlate call information from multiple sources to facilitate the billing and revenue settlement process with their customers and other service provider partners.
- Open APIs: The Cisco TelePresence Exchange System enables further integration of third-party and internally developed applications to deliver customized meeting experiences and industry applications for Cisco TelePresence collaboration systems. For example, the scheduling API enables a third-party scheduling application to schedule, modify, or cancel point-to-point and multipoint meetings. Depending on the types of endpoints joining a meeting, the appropriate media resources are selected from the media resource infrastructure, optimizing performance, minimizing conferencing port costs, and simplifying the user experience.
Services and Customer Experience
- One-button-to-push experience: The Cisco TelePresence Exchange System preserves ease-of-use features such as one-button-to-push session initiation for hosted Cisco TelePresence services. The system automatically provisions endpoints hosted in the service provider cloud with the one-button-to-push information necessary to either directly dial another endpoint or authenticate and join a prescheduled multipoint conference without any need for additional user interaction.
- Advanced conferencing: The system offers a prepackaged multimedia meet-me or virtual meeting room conferencing service enabler that uses instances of Cisco TelePresence Server and Cisco TelePresence MSE 8000 MCUs to deliver full endpoint interoperability while minimizing total cost per port. It supports a scheduled, rendezvous, and impromptu paradigm with a dial-in and dial-out model to allow service providers to properly tailor the service based on their customers' needs. It also takes advantage of the internal VoiceXML engine of the system to create a pool of IVR instances in the scenarios where it is necessary to interact with the end user for authentication and user notification. The system also allows you to extend scheduled meetings beyond the scheduled end time. You can extend a meeting for a configured interval, giving you flexibility and control to manage your meetings.
- Business-to-business communication: The system is designed to securely support multipoint and point-to-point calls across enterprise and service provider boundaries. It can route scheduled and impromptu point-to-point calls between different organizations through the service provider cloud using an internal number routing database.
- Interoperability services: The system supports network-based video interoperability with traditional video systems, telepresence solutions or any standards based video-enabled device using the Cisco TelePresence MSE 8000 Series in a multitenant architecture for optimum service scalability and reach.
- Active meeting management capabilities: Active meeting management controls allow you to add and drop participants, lock and unlock meetings, mute and unmute participants, and change layout, roster, etc. Service providers can offer a concierge-based service using the Cisco TelePresence Exchange Web Admin Graphical User Interface (GUI) with active meeting management controls or develop an application based on the AMM APIs for end-customer use.
- Multilanguage IVR: The system offers multiple language options to help customers in different languages to attend the same meeting. The IVR system can be associated with many languages through different service access numbers.
- Interprovider communication: The system conforms to a policy and resource-management framework for interprovider connectivity. It facilitates the process by which service providers can peer with other service provider partners' networks with the intent of increasing the service reach for their business customers while maintaining a consistent user experience across enterprise and service provider boundaries.
Architecture:
Design of the Cisco TelePresence Exchange System is based on a modular architecture with integrated media and service control, and hosted applications to optimally deliver and scale global and regional deployments. The system supports distributed network architecture and brings network topology awareness to the service delivery, optimizing network economics by pushing the media handling and processing as close as possible to the business customer while delivering a superior experience. The system architecture is designed to match service providers' scalability, resiliency, and availability requirements. It provides a fully redundant solution where resiliency and high availability can be delivered for all network, call-control, and media server products.
A single Cisco TelePresence Exchange System deployment can centrally manage globally distributed deployments where scheduling applications can apply intelligent resource selection to choose the most appropriate region or location to host each meeting. Such capabilities allow service providers to concentrate network traffic within regions and reduce total network cost.
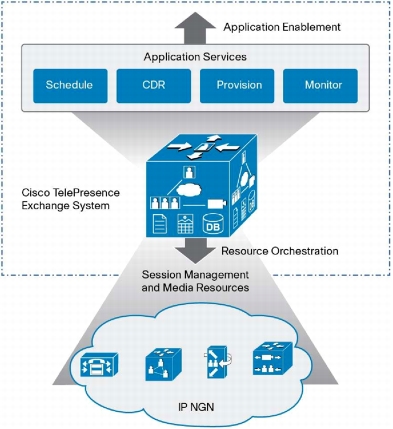
System Architecture
Technical Specifications:
| Product Specifications |
| System management |
- Cisco TelePresence Exchange Administrator user interface
- Secure Shell (SSH) Protocol command-line interface (CLI)
|
| Performance and scalability |
- Up to 2400 concurrent telepresence sessions
- Up to 40 telepresence sessions per second in sustained mode
- Up to 10 scheduling or billing API requests per second in sustained mode
|
| Reliability and availability |
Fully redundant multitiered system with every tier in either an active-active or active-standby configuration |
| Alarms and reporting |
- Resource MIBs support to enable easy monitoring of solution components
- Platform MIBs support to enable hardware-level monitoring
- Event reporting on the Cisco TelePresence Exchange user interface to enable easy troubleshooting
- Cisco TelePresence TX series, TC series, TE Series, Jabber®, and Cisco Video phones (includes Cisco TelePresence System 3000 [CTS 3000], Cisco TelePresence System 1x000, and 500 series)
|
| Supported Cisco and third-party endpoints |
Standards-based Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), H.323 telepresence standard, and standard- and high-definition (SD and HD, respectively) video endpoints
*Not supported in Hosted service deployment model |
| SIP |
Support for SIP RFCs 2543 and 3261 |
| Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) and HTTP |
Support for SOAP- and HTTP-based Web Services API for integration with scheduling and billing systems |
| H.323 |
H.323 support, achieved using Cisco TelePresence MSE 8510 and MSE 8710 for interoperability dial-out; dial-in is supported through SIP conversion at the enterprise edge (through the Cisco TelePresence Video Communication Server Expressway [Cisco VCS Expressway]) |
| ISDN |
ISDN support, achieved using Cisco TelePresence MSE 8321 ISDN blade |
| Northbound and southbound |
- SOAP-/HTTP-based Web Services API for scheduling, CDRs, and active meeting management
- XML/remote-procedure call (RPC) for managing Cisco TelePresence MSE and Cisco TelePresence Multipoint Switch resources
|
| APIs |
AXL/SOAP/Secure FTP (SFTP) for Cisco Unified Communications Manager integration |
| SNMP |
SNMPv2c, SNMPv3, and SNMP Traps |
| Cisco Discovery Protocol |
Full support, including neighbor discovery (and SNMP support) and Cisco Discovery Protocol advertisement |
| MIBs |
- CISCO-CDP-MIB
- CISCO-SYSLOG-MIB
- IF-MIB
- IP-MIB(v2)
- RFC1213-MIB
- SNMPv2-MIB
- TCP-MIB
- UDP-MIB
- SNMP-FRAMEWORK-MIB
- SNMP-MPD-MIB
- SNMP-VACM-MIB (SNMP-VIEW-BASED-ACM-MIB)
- SNMP-NOTIFICATION-MIB
- SNMP-TARGET-MIB
- SNMP-USER-BASED-SM-MIB
- HOST-RESOURCE-MIB
- IBM-SYSTEM-AGENT-MIB
- IBM-SYSTEM-ASSETID-MIB
- IBM-SYSTEM-HEALTH-MIB
- IBM-SYSTEM-LMSENSOR-MIB
- IBM-SYSTEM-MEMORY-MIB
- IBM-SYSTEM-MIB
- IBM-SYSTEM-NETWORK-MIB
- IBM-SYSTEM-POWER-MIB
- IBM-SYSTEM-PROCESSOR-MIB
- IBM-SYSTEM-RAID-MIB
- IBM-SYSTEM-TRAP-MIB
|
Components
The Cisco TelePresence Exchange System can be configured in a physical hardware-based model (based on IBM x3650-m2) or virtualized on the Cisco UCS B200 M3 Series Blade.
| |
Server Based |
Virtualized Tested Configuration* |
| Components |
Six Cisco TelePresence Exchange System servers (based on IBM x3650m2) |
Two Cisco UCS Server Blades: Model: B200 M3 D
CPU for each blade: 2 Xeon E5-2690 (two 8-core CPUs at 2.9 GHz) |
| Connectivity |
Two Gigabit Ethernet RJ-45 ports |
One Gigabit Ethernet RJ-45 port |
| Memory |
8 GB on each server |
RAM: 64 GB on each blade |
Physical dimensions
(H x W x D) |
Six servers, each 2 rack units (2RU): 1.7 x 17.3 x 28.0 in. (711.4 x 43 x 440 mm) |
Variable based on Cisco UCS server rack selected |
| Approval and compliance |
U.S.: Safety: UL60950-1 2nd edition 21CFR1040
EMC: FCC Part 15/CISPR22 Class A |
EMC SAN specifications: 200-300 input/output operations per second (IOPs) and 300-GB fastcache
*Capture from data sheet
- EMC storage area network (SAN) specifications: 200-300 IOPs and 300-GB fastcache
- Local storage: Dual Attachment Stations (DAS) (Redundant Array of Independent Disks [RAID] 1) for VMware Hypervisor installed on local disk
|



