Overview:
The Cisco TelePresence Video Communication Server (Cisco VCS) simplifies session management and control of telepresence conferences. It provides flexible and extensible conferencing applications, enabling organizations to benefit from increased employee productivity and enhanced communication with partners and customers.
The Cisco VCS delivers exceptional scalability and resiliency, secure communications, and simplified large-scale provisioning and network administration by taking advantage of Cisco TelePresence Provisioning 2.0 capabilities.
The Cisco VCS interworks seamlessly with Cisco Unified Communications Manager (Cisco UCM), bringing rich telepresence services to organizations with Cisco UCM. It also offers interoperability with third-party unified communications, IP telephony networks, and voice over IP (VoIP) systems.
The Cisco VCS is available as an appliance or as a virtualized application on VMware, with additional support for Cisco Unified Computing System™ (Cisco UCS™) platforms.
You can deploy the Cisco VCS as the Cisco TelePresence Video Communication Server Control (Cisco VCS Control) for use within an enterprise and as the Cisco TelePresence Video Communication Server Expressway (Cisco VCS Expressway) for external communication (Figure 2). The Cisco VCS Expressway includes the features of the Cisco VCS Control, augmented with highly secure firewall-traversal capability. An alternative solution, suited to small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs), is the Cisco VCS Starter Pack Express. Optional packages that you can deploy include Cisco TelePresence FindMe (FindMe), Device Provisioning, and Dual Network Interfaces (Cisco VCS Expressway only).
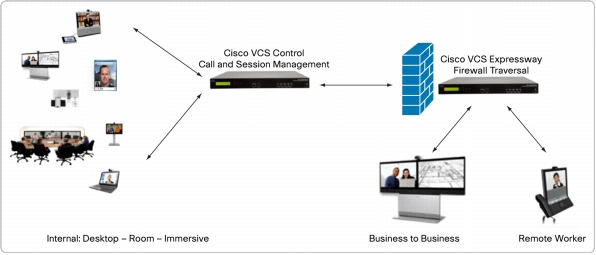
Figure 2. Cisco VCS Control and Cisco VCS Expressway
Cisco VCS Control
Cisco VCS Control delivers any-to-any enterprise wide conference and session management and interworking capabilities. It extends the reach of telepresence conferences by enabling interworking between Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)- and H.323-compliant endpoints, interworking with third-party endpoints; it integrates with the Cisco UCM and supports third-party IP private branch exchange (IP PBX) solutions. Cisco VCS Control implements the tools required for creative session management, including definition of aspects such as routing, dial plans, and bandwidth usage, while allowing organizations to define call-management applications, customized to their requirements (Figure 3).
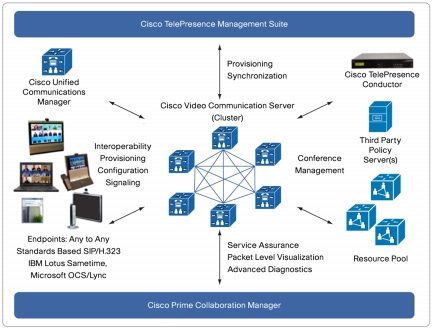
Figure 3. Cisco VCS Control in the Network
Features and Benefits:
Benefits of Cisco VCS follow:
- Greater reach: Any-to-any interoperability facilitates smooth video communications between standards-based and third-party client users.
- Efficient conference management: Administrators can proactively monitor and configure conferences through intuitive web user interfaces to optimize bandwidth usage in real time, helping to deliver a flawless video experience.
- Highly scalable: With features such as clustering and policy services integration, the Cisco VCS is architected to support enterprise growth, with smooth expansion as usage increases, protecting investment in video infrastructure.
- Contact location: Use FindMe to ensure that people can always be contacted.
- Extended telepresence capability: Integration with Cisco UCM helps reduce complexity for users and facilitates interworking between SIP- and H.323-compliant endpoints within an enterprise, regardless of individual endpoint capabilities.
- Reduced footprint: This solution incorporates presence server, H.323 gatekeeper, SIP proxy, and SIP registrar capabilities.
- Secure: The industrially recognized secure performance of Cisco VCS provides administrators with complete confidence in their network security.
- Differentiation: Through policy services integration and dial plan configuration, you can create flexible telepresence solutions that you can customize to deliver value and meet ever-increasing customer requirements.
- Flexibility: Administrators can implement the Cisco VCS as either an appliance or a virtualized application to meet the needs of their organizations.
Features of Cisco VCS follow:
- SIP registrar, SIP proxy server, presence server, and presence user agent: The Cisco VCS supports the SIP protocol, acting as a SIP registrar, storing the Address of Record of registered endpoints, and forwarding SIP requests as a SIP proxy server. The Cisco VCS supports the SIP for Instant Messaging and Presence Leveraging Extensions (SIMPLE) protocol, and can act as a presence server and presence user agent.
- H.323 Gatekeeper: The Cisco VCS provides H.323 Gatekeeper functions. It accepts registrations from H.323 endpoints and provides call-control functions such as address translation and admission control.
- Interoperability and Interworking: The Cisco VCS provides interoperability between SIP and H.323 standards-compliant endpoints, and also supports communication with IBM Lotus Sametime and Microsoft Office Communicator Server (OCS) and Microsoft Lync endpoints.
- IPv4 and IPv6: The Cisco VCS supports IPv4 and IPv6, with IPv4 and IPv6 Interworking.
- Zone and bandwidth management: The Cisco VCS supports management of the allocation of bandwidth between sites, endpoints, and groups of endpoints. You can specify the amount of bandwidth available for intra- and inter- zone calls, allowing you to control the way in which bandwidth is used and calls are prioritized. Features of the Cisco VCS bandwidth management capability include the following:
– Flexible, customizable zone configuration with named zone and default zone
– Bandwidth management on both a per-call and a total-usage basis, configurable separately for calls within local subzones and to neighboring systems and zones
– Automatic down-speeding option for calls that exceed the available bandwidth
– Preconfigured defaults for:
- Cisco UCM neighbor zones
- Cisco TelePresence Advanced Media Gateway
- Microsoft OCS 2007 and Microsoft Lync neighbor zones
- Nortel Communication Server neighbor zones
- Dial plan and call-routing control: The Cisco VCS allows administrators to create dial plans to define the way in which calls are handled within the network. Transforms can be applied to source and destination address information to define general routing rules. Dial plans can be based on call aspects such as:
– Source or destination address, zone, or subzone configuration
– Call policy for authenticated or nonauthenticated endpoints
– FindMe™ configuration
- Authentication: You can configure the Cisco VCS to allow both authenticated and unauthenticated endpoints to register to the same VCS, and to subsequently control the operation of those endpoints based upon their authentication status. The Cisco VCS supports:
– H.325 authentication
– SIP digest authentication
– Windows NT LAN Manager (NTLM) authentication
– Control over which endpoints are allowed to register through allow and deny lists
– Microsoft Active Directory (AD) integration for Cisco TelePresence Movi
– Administrator authentication through Active Directory
– Integration with Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)-accessible H.350 directories
- Policy services: A policy services interface is available to allow you to define call policies to be applied within your organization. For example, you can handle calls differently according to time of day, source or destination address, or more complex algorithms. The policy services interface supports Call Processing Language (CPL).
- Clustering: The Cisco VCS can function as a standalone system or in a cluster configuration for increased capacity and redundancy. Cisco VCS clustering supports:
– Clustering of up to six Cisco VCS peers
– Sharing of call licenses within a cluster
- Administration: The Cisco VCS provides administrative interfaces to allow setup, administration, and monitoring of the network configuration. Administrative features of the Cisco VCS follow:
– Embedded setup wizard for initial configuration
– System and status overview
– Advanced diagnostics support
– System administration through a web interface, Telnet, Secure Shell (SSH) Protocol, and Secure HTTP (HTTPS)
– Integration with the Cisco TelePresence Management Suite (TMS) for scalable provisioning and configuration
Optional features follow:
- Cisco TelePresence FindMe
- Cisco TelePresence Multiway
- Device provisioning
- Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 Enhanced Interoperability option
- Advanced Account Security Joint Interoperability Test Command (JITC)
Capacity of one Cisco VCS follows:
- Up to 2500 registrations
- Up to 500 nontraversal calls
- Up to 100 traversal calls
- Up to 1000 subzones
Capacity of a cluster of six Cisco VCSs follows:
- Up to 10,000 registrations
- Up to 2,000 nontraversal calls
- Up to 400 traversal calls





